Chapter 1:
> Point, line, and polygon data is also known as vector data
> Collecting measured values for any location on the Earth’s surface to form a digital surface is known as a raster.
Chapter 2:
> .aptx is the typical project template
>.aprx is a project file
>.ppkx is a project package
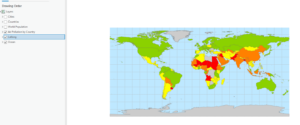
> The contents pane allows you to modify a map’s layers
> Learned how to select individual features
> Learned how to change feature symbols, display feature symbols, use the measure tool, and package my project to share online.
> Learned how to convert a 2D map to a 3D one
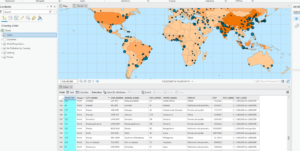
Chapter 3:
> An attribute query is a request for features in a table that meet user-defined criteria.
> Using an attribute join operation, we can join the spreadsheet table to the existing attribute table, as long as there is a common attribute field in each table
> Columns are often called fields.
> Fields include Object ID, which is a unique identifier assigned to every row in a table
> A layer file is a saved symbology scheme that points to a specific source datasheet
> A layer package bundles the layer file along with the source data
> Joining data based on location is a spatial join- this allows you to define a spatial relationship between two layers and combine their attributes in a new output layer

Chapter 4:
> A shapefile stores geometry and attribute data for one feature
> A geodatabase is a storage container where sets of features are stored into feature classes
> Nonspatial tables do not have well-defined geometry as feature classes do
Chapter 5:
> Python is a coding language that is compatible with ArcGIS
> You can define a workflow in the ‘tasks’ pane