Chapter 4
- database- container for the data of an organization, project, or other undertaking for record keeping, decision-making, analysis, or research
- geodatabase is Esri’s database for geospatial data
Tutorial 4-1
- software automatically creates geodatabase when you start an ArcGIS project
- can connect to other folders for easy access
- shapefile- spatial data format for a single point, line, or polygon layer
Tutorial 4-2
- much of what is displayed by GIS depends on attributes- columns of data in tables
- you can download data from external sources (ex: US Census Bureau) to map
- added a column to Tracts attribute table
Tutorial 4-3
- GIS links tabular data to spatial features in feature classes
- SQL criterion: attribute name <logical operator> attribute value
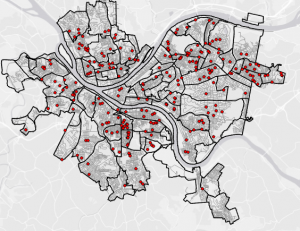
Tutorial 4-4
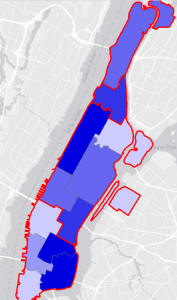
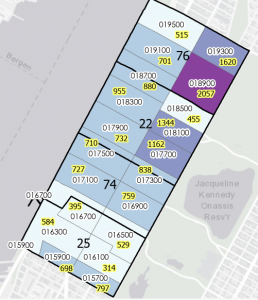
- count burglaries by neighborhood
- created choropleth map based on the join count I added
Tutorial 4-5
- GIS creates central points when you use graduated colors for symbology for polygon layer
- created fields to find coordinates of central points
- Feature to Point calculates central points instead of centroids
Tutorial 4-6
- creating code table and necessary fields/data
Chapter 5
- learn about latitude and longitude coordinates and their geographic coordinate system
- map projections- making flat maps from the nearly spherical earth
Tutorial 5-1
- Longitude: 0-180 east to west
- Latitude: 0-90 north to south
- 100+ map projection in GIS
- graticule- networks of lines on the map (30-degree intervals east-west and north-south)
- changed map shape
Tutorial 5-2
- working with US map projections
- Albers equal-area standard projection for US Geographical Survey (USGS) and US Census Bureau for US maps
- larger part of world you need the more distortion
Tutorial 5-3
- Foe medium/large scale maps use localized projected coordinate systems specific to the study area
- need to use a reference map to determine what zone you are in to apply the correct coordinate systems
- adding layer adopted new coordinate system to the map
Tutorial 5-4
- review file formats for vector spatial data
- GPS and many other databases provide coordinates with x,y values
- KML is the file format used to display geographic data in many mapping applications (international standard for Open Geospatials Consortium)
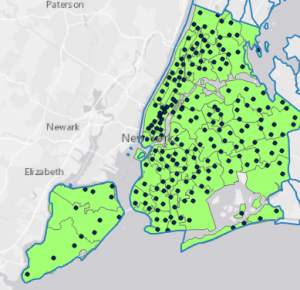
Tutorial 5-5
- use data from US Census Bureau
- learned how to clean up data in Excel
- trying to export files into the ArcGIS crashed my computer and I had to restart it and couldn’t finish the tutorial
Tutorial 5-6
- rasters are large files and should probable be stored elsewhere
- Bicycle Count Stations wasn’t there where it said it would be
Chapter 6
- geoprocessing- framework and set of tools for processing geographic data
Tutorial 6-1
Tutorial 6-2
- workflow for creating study region from layers that have more features than needed
- created feature class from selected features
Tutorial 6-3
- merging water features into a new single layer
Tutorial 6-4
- use Append tool to add features to an existing feature class
- Added FireHouses and PoliceStations to the attribute table
Tutorial 6-5
- intersecting features to determine streets in company fire zones
Tutorial 6-6
- Union tool overlays geometry and attributes of two input polygon layers to generate a new output layer
Tutorial 6-7