Hello, my name is Evelyn VanderVelde. I am a senior from Holland, Michigan majoring in environmental science and minoring in botany.
- for my assignment this week, I already have a account made from the 191 class with Krygier and my Intro is above. I updated my Bio so now y’all can know some basic things about me.
- In my blog I found all of my assignments from 191 as well as that the website format has updated and these knew posts are bugging me. I liked the last formatting of the posts to be much easier because they were more simple.
Things I learned from the ArcGIS webpage, Get started: what is ArcGIS online ->
- Share and Collaborate – I learned that sharing your maps on ArcGIS online is easier with the groups that are private. I have some experience with groups with my job with the Michigan DNR this past summer. As well as making collaborations with other groups to share each others maps and work on each others content. Other ways to share maps and other content include embedding them in web pages, on blogs, in web apps, and through social media. Use focused apps to collaborate with colleagues in the field, office, or community.
- Be mobile in the field- On arcGIS online you can also access your maps in your mobile device whether this be a tablet or smart phone. Meaning that data can be collected directly from the field onto the map itself and updated to the entire crew in real time.
Training course:
- I found that I learned about exploring a 3D scene
- I also learned that when you move to a different bookmark in one of the tutorials that the base-map changes from Topographic to Imagery
Two articles:
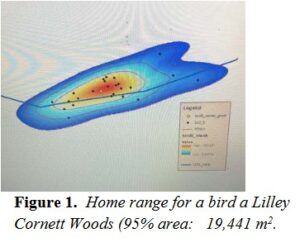
- for the first article i looked up arcOnline hemlock because that is one of my favorite trees. In THIS article they used arcOnline to create a spot map of the home range for a species of bird that nests in Eastern hemlock trees.
- For my second article I looked up ArcOnline Michigan coast and found THIS link from a Michigan state grad students thesis project. This article did not include any of the maps that they used to collect their data besides an image from one of their Arial images collect by a satellite about the declining coast of lake Michigan in correlation to human infrastructure.

Delaware data Inventory is already completed.



 Two articles:
Two articles:

 Delaware data Inventory is already completed.
Delaware data Inventory is already completed.