Chapter 6: Spatiotemporal Data and Real-time GIS
Real-time GIS handles objects and events that move, appear, and change throughout time. Real-time data needs real-time GIS to locate/track targets and store, manage, search, display, and analyze data. Spatiotemporal data comes from various sources and can be categorized into the following groups: moving, discrete, stationary, and change. The key terms to know and understand while working with spatiotemporal data are: time measurement systems (units), time reference systems (time zones/daylight savings), time representations (arrangement of date/time), and temporal resolution (time interval of sampled events). IoT refers to the network of physical objects (various devices, airplanes, taxis, bicycles, lights, sprinklers, etc.) embedded with sensors and network connectivity that allow these objects to collect/exchange data. ERSI’s geospatial cloud provides users with ArcGIS Velocity and ArcGIS GeoEvent Server with real-time GIS. Both can meet the requirements to collect, process, and store high-volume and high-velocity real-time data generated by IoT. ArcGIS Velocity and GeoEvent Server share similar basic components: ingest, process, and outputs. However, ArcGIS is a relatively new real-time GIS product and introduces new types of items to ArcGIS: feed items, real-time analytics items, and big data analytic items.
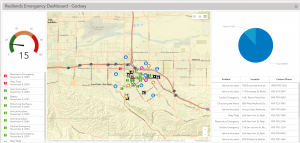
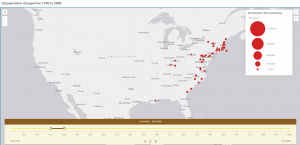
Application Idea: Create a dashboard app to monitor the smart Survey123 form to better understand students’ interests on the Ohio Wesleyan Campus.