Chapter 5
-
- ArcGIS Enterprise and ArcGIS Online have similar functions but Enterprise runs on user-managed infrastructures
- Enterprise used when:
- Need for on premises Web GIS
- Need for hybrid Web GIS
- Need for functionalities only on ArcGIS Enterprise
- Enterprise pretty much a variation of Online
- Portal for ArcGIS provides ability to:
- Create various types of hosted layers.
- Create, save, and share web maps and scenes.
- Create and host web-mapping apps.
- Search for GIS content within your organization.
- Secure the access to your GIS content.
- Manage organizational utility services.
- ArcGIS Server- create and host various types of geospatial web services which allows for a server computer to receive and process requests sent by various clients
- ArcGIS Web Adaptor- integrates ArcGIS Enterprise with organization’s existing web server and security mechanisms
- ArcGIS Data Store- allows for data storage configuration for hosting services with ArcGIS Enterprise
- Deployment scenarios for ArcGIS Enterprise
- Single-machine deployment
- Multitiered deployment
- Highly available deployment
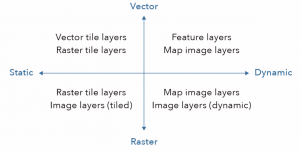
- Raster tile layers provide maps to client applications as image files
- Appropriate for basemaps and maps with little change
- Vector tile layers deliver map data as many grouped vector files
- Map image layers can be drawn by the server or by using tiles from a cache
- Feature services generate feature tiles when requested by client apps
- When a user requests a map of a certain extent, 16 feature tile requests will actually be created and cached
- Image layer requests not usually reusable
- Standards specify the interface that different vendors should use and are important to establish interoperability among vendors
- When using Enterprise make sure data is accessible by Enterprise (not always is like when you import data with Online)
- I could use the information from this chapter to provide a map of schools in the Cleveland area and have links to their school websites attached. This could help parents of young children when they are trying to decide where to raise their kids.
Chapter 6
-
- Spatiotemporal data can be categorized into four categories: moving, discrete, stationary, and change
- Real-time GIS- GIS that handles current and continuous data
-
- Value of event can be point in time or duration of time
- Key terms for spatiotemporal data:
- Time measurement systems
- Time reference systems
- Time representations
- Temporal resolution
- IoT– network of physical objects embedded with sensors and network connectivity that enable these objects to collect and exchange data
- Smart city- uses IoT devices to supply information that will assist the city in managing assets and resources efficiently
- Smart homes- houses with wifi-connected devices used to enhance the function of the home
-
- ArcGIS Velocity and GeoEvent Server share components:
- Ingest- provide ways to communicate with IoT platforms, sensor networks, social network feeds, and other real-time data streams
- Process- processes real-time data received and translated by the ingestion component
- Outputs- sends processed data to variety of destinations
- ArcGIS Velocity introduces new types of items:
- Feed items
- Real-time analytic items
- Big data analytic items
- ArcGIS Velocity and GeoEvent Server share components:
- Poll- client periodically polls server to retrieve the latest data
- Push- push data to web client (used by ArcGIS)
- ArcGIS Dashboards provides common view of systems and resources you manage
- I could use the information from this chapter to create a map that monitors police activity in my hometown city Berea, Ohio. By doing this, people could use the map to be aware of where they might have run-ins with law enforcement